Table of contents
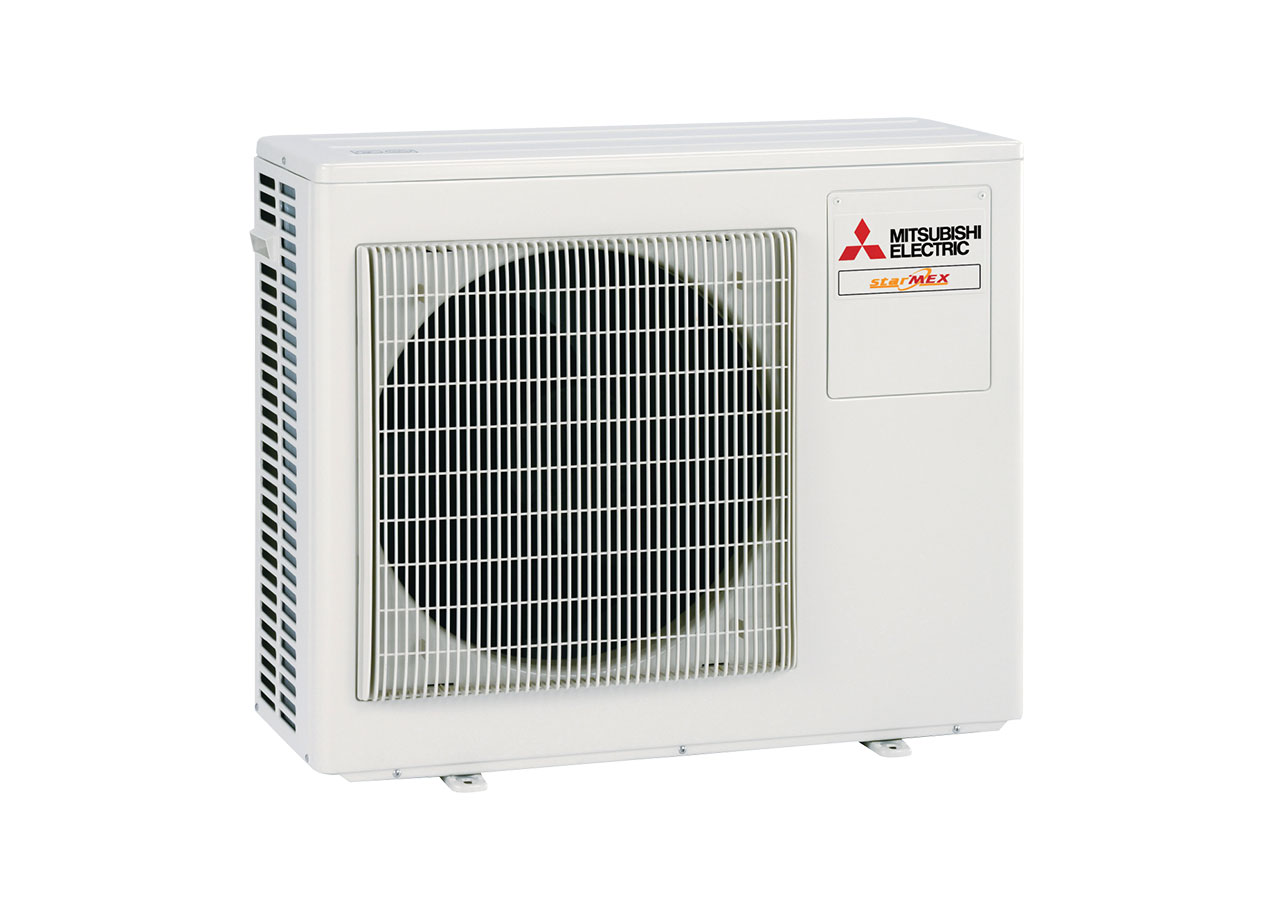
Inverter technology
How does an inverter work?
The inverter controls the voltage, amperage, and frequency of electrical equipment, for example, a compressor's motor in a refrigeration system. They get information from sensors that keep an eye on operating parameters and the speed of the compressor's rotation. This lets them directly change how much power the refrigeration system puts out. Closely watching the operating frequency stops much energy from being used and gives the user the most comfort.
New-style DC motor
The "Poki-Poki Motor" from Mitsubishi Electric is made with "densely concentrated winding," which creates a high-performance magnetic cushion core.
PAM Technology
PAM is a technology to control the current intensity wave shape that closely resembles the wave shape of the voltage, increasing the efficiency of electricity use. With PAM technology, 98% of the input voltage is effectively used.
Power receiver and control system two solenoid throttle
Mitsubishi Electric has made a power receiver and two throttle control circuits to maximize compressor capacity. This technology ensures instantaneous monitoring and feedback on the output current and temperature waveforms. Operational efficiency is also increased by adapting the system to the characteristics of the R410A refrigerant.
For the heat exchanger, the refrigerant tube with grooves inside increases the area where heat can move.
Conductor/pipeline test function
With the push of a button, the piping and wiring will be checked to see if they are correctly connected. A correction is performed automatically if a conductor is found to be faulty.
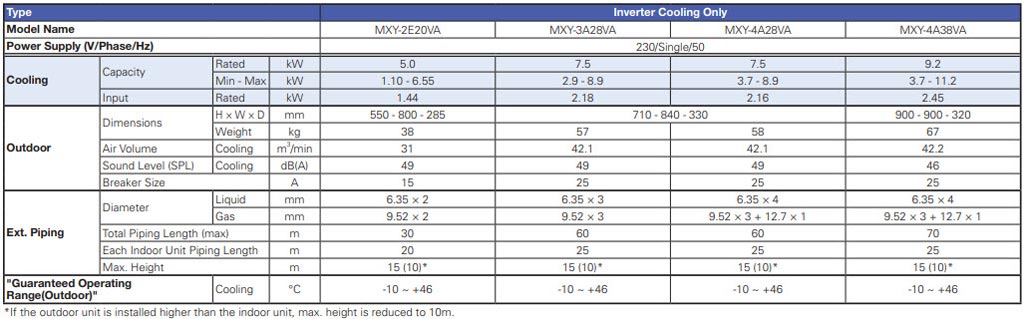
Specifications